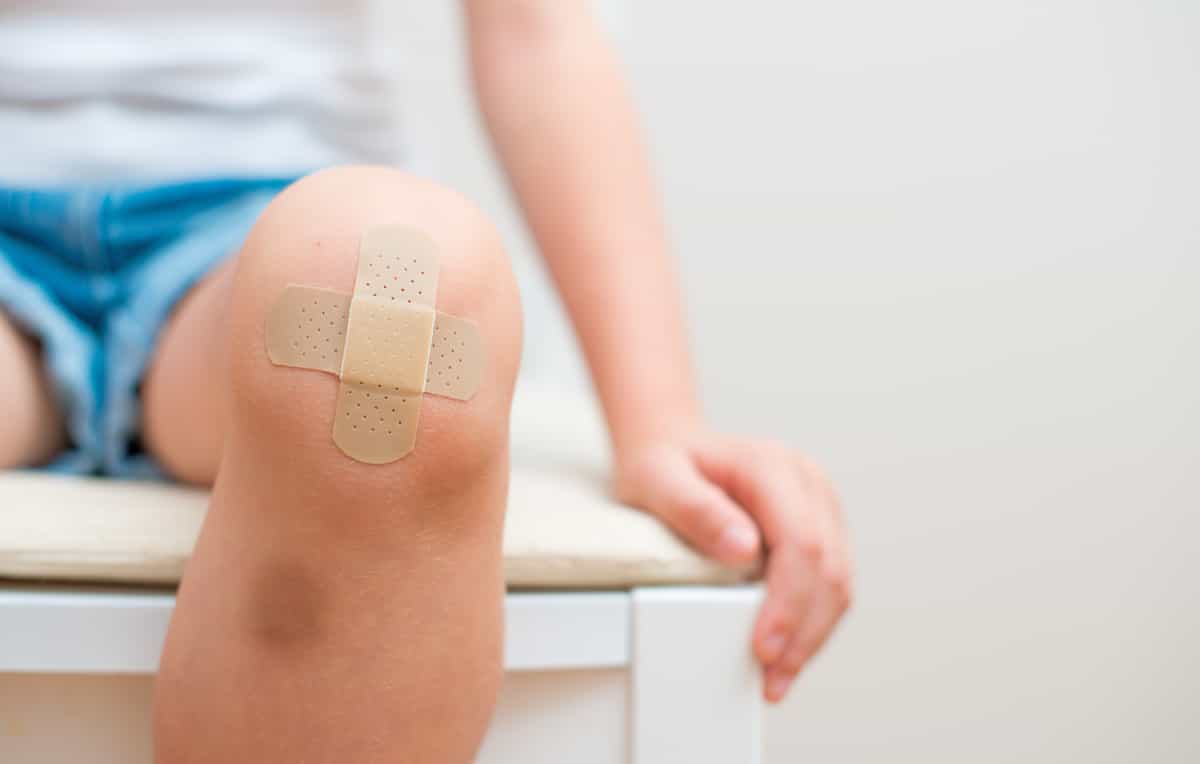
Definition
- Injuries to the skin anywhere on the body surface
- Includes cuts, scratches, scrapes, bruises and swelling
Types of Skin Injury
- Cuts, lacerations, gashes and tears. These are wounds that go through the skin to the fat tissue. Caused by a sharp object.
- Scrapes, abrasions, scratches and floor burns. These are surface wounds that don’t go all the way through the skin. Scrapes are common on the knees, elbows and palms.
- Bruises. These are bleeding into the skin from damaged blood vessels. Caused by a blunt object. They can occur without a cut or scrape.
When Sutures (Stitches) are Needed for Cuts
- Any cut that is split open or gaping needs sutures.
- Cuts longer than ½ inch (12 mm) usually need sutures.
- On the face, cuts longer than ¼ inch (6 mm) usually need to be seen. They usually need closure with sutures or skin glue.
- Any open wound that may need sutures should be seen as soon as possible. Ideally, they should be checked and closed within 6 hours. Reason: to prevent wound infections. There is no cutoff, however, for treating open wounds.
Cuts Versus Scratches: Helping You Decide
- The skin is about 1/8 inch (3 mm) thick.
- A cut (laceration) goes through it.
- A scratch or scrape (wide scratch) doesn’t go through the skin.
- Cuts that gape open at rest or with movement need stitches to prevent scarring.
- Scrapes and scratches never need stitches, no matter how long they are.
- So this distinction is important.